- Technical analysis or TA is the study of the past movements of financial markets and securities including price and volume.
- Fundamental analysis focuses on figuring out the true value of stocks.
- Fundamental Analysis vs Technical Analysis has several similiarities and differences
Technical analysis is a systematic way of analyzing and studying financial markets to make informed trading decisions. Technical analysis has been in practice for centuries, however, it has become extremely popular in the 21st century. Nowadays, data science and tools have become more advanced. Today, it is the age of the internet and more people have access to data and advanced tools to make informed trading decisions. Read below for the Technical Analysis vs Fundamental Analysis match.
Fundamental analysis, price action, and value investing are some other major schools of thought to approach financial markets. However, they are many differences between all those analysis approaches and all have advocates and adversaries. Let’s first discuss how technical analysis is different from fundamental analysis.
What is technical analysis?
Technical analysis or TA is the study of the past movements of financial markets and securities including price and volume. It works on the simple principle that history repeats itself. That means the financial markets have a tendency to move in repeated and consistent patterns. So, through study and analysis of the past price and volume movements, those patterns are identified and their future movements are predicted. This information is extremely useful that enables investors to make informed decisions.
The technical analysis captures a complete picture of a company and demands a focus on price data and movements. You need to observe market trends and patterns to predict the market’s future movements. You may use the following technical indicators to conduct technical analysis.
- Moving averages to determine the direction of the current market trend.
- Exponential moving averages to confirm crucial movements of the market and measure their authenticity.
- Moving average convergence/divergence to detect fluctuations in momentum.
- Average directional index to gauge the strength of the current market trend.
- Standard deviation to measure the magnitude of the price movement.
- Relative strength index to identify momentum and market conditions.
- Fibonacci retracement to determine how much a market will deviate from its current trend.
- Bollinger bands to predict long-term price movements.
- Stochastic oscillator to determine momentum and trend strength.
Also indicators some times are used to spot divergences (when the indicator and price does move together).
What is fundamental analysis?
Fundamental analysis focuses on figuring out the true value of stocks. The fundamental analysis gives a reasonable estimate of the intrinsic value of a stock. You need to consider both qualitative and quantitative factors to conduct a thorough fundamental analysis.
Qualitative factors
Qualitative factors are:
- News regarding the company you want to invest in is crucial and can make prices rise or fall. Good and bad news affect supply and demand and finally stock prices.
- Personnel and management changes are equally important as they affect the perception of the market. Such changes directly affect the reputation of a company and ultimately stock prices.
- Economic and financial events are also crucial as they may cause higher volatility and market uncertainty.
Quantitative factors
Quantitative factors include:
- Earning reports are important as a quantitative factor during fundamental analysis. Traders should track earning reports and releases to keep an eye on changes in the company’s earnings. It is crucial to note whether the stock price reflects the new earning level or not. If it doesn’t, that means the stock price doesn’t reflect true value.
- Balance sheets reflect earning potential of a company and are a good source to judge a company.
- Dividends and other important ratios are also very helpful to analyze a company and its earning potential. P/E ratio, D/E ratio, ROE, current ratio, earnings yield, relative dividend yield, and price-earnings to growth (PEG) ratio are important figures to look at.
How technical analysis is different from the fundamental analysis?
Comparison of technical analysis and fundamental analysis is a very broad topic that requires pages. There are a lot of differences between these two approaches. In fact, they both are at the opposite ends of the spectrum. However, we have tried to boil down this broad topic of technical analysis vs fundamental analysis into the following key points.
Intrinsic value
Fundamental analysis works with the objective of evaluating the intrinsic value of a particular stock or security. Whereas, technical analysis works with the objective of predicting the prices of stocks or securities in the future.
Real value vs consensus
The fundamental analysis gives the present actual value of a stock. On the other hand, technical analysis analyzes the price movements of stocks with the objective of forecasting future price movements.
Pick or timing
Fundamental analysts use fundamental analysis for investment purposes. Conversely, a trading function is the major use of technical analysis.
Broad factors vs price
The fundamental analysis employs various economic factors for analysis whereas technical analysis uses price, patterns, and trends for analysis.
Context vs price
Economic reports, news events, balance sheets, income statements, industry statistics, etc. feed data for fundamental analysis. On the other hand, chart analysis is the major source for data extraction in technical analysis.
Future vs past
Fundamental analysis takes into account historical as well as present data. Conversely, the technical analysis only considers past data.
Timeframe
Long-term traders often use fundamental analysis for their investments. On the other hand, swing and short-term traders often prefer technical analysis.
Fundamental analysis is often preferred while making long-term investment decisions. Conversely, technical analysis is used for short-term investment decisions.
Both analysis impact the other
Any external news doesn’t impact fundamental analysis as it impacts technical analysis.
Price encompasses it all
Fundamental analysis uses returns on assets and returns on equity concepts. Whereas, technical analysis uses price data and Dow Theory for analysis.
Asset based or price based
The fundamental analysis emphasizes both factors, quantitative and quantitative. While technical analysis has its main focus on price, volume, moving averages, charts, etc.
Technical analysis vs price action
Technical analysis is also different from price action. Price action trading is a way of day trading to make trading decisions through analyzing price movements. It doesn’t rely on indicators used by technical analysis. Technical analysis involves the study of charts, trends, and patterns but price action delves deeply. It tends to decipher those underlying factors that cause things to happen. It actually sheds light on those factors that move stock prices up or down.
Advocates of price action believe that technical analysts use various unnecessary variables. They believe that all those factors are in fact derivatives of price action itself. So, why should we waste time on all that noise? They suggest analyzing price action in the first place to predict future price movements. They heavily believe and rely on raw, natural price data that all financial markets supply free of cost. Breakout, candlesticks, trends, and areas of support/resistance are the major price action trading tools.
Technical analysis vs value investing
Value investing is another investment strategy that revolves around finding those stocks or securities that are being traded less than their intrinsic value. The users of value investing the search for those stocks or securities that the stock market underestimates. Value investors don’t follow the herd. They use financial analysis and believe in long-term investment in quality companies.
The major difference between technical analysis and value investing is the timeframe. Technical analysis is a short-term approach while value investing is a longer-term investing strategy. Technical analysts only look at charts and graphs to make investment decisions. On the other hand, value investors look at business and economic concepts to make decisions. Moreover, technical analysis looks only backward and future market conditions are totally ignored. Value investors believe that you can’t trade on expectations. You cannot expect that what has happened in the past will recur.
Final thoughts
Technical analysis, fundamental analysis, price action, and value investing are all widely used financial market analysis techniques. They all have advocates as well as adversaries. They all have pros and cons. When to use technical analysis? Or when to use any other analysis strategy? That depends on a trader’s overall trading plan and preferences. We have highlighted major differences between all those strategies. Now, the choice is yours to choose the strategy that suits your trading plan and preferences.
 Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
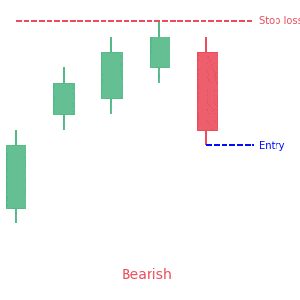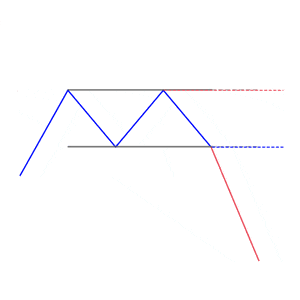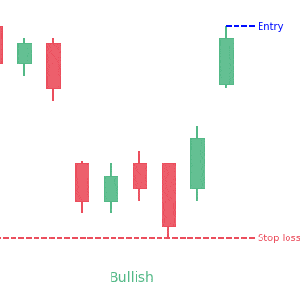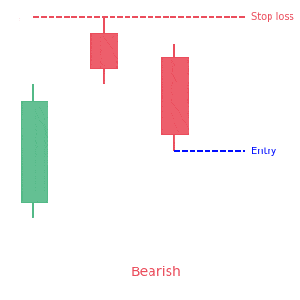 We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!
We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!