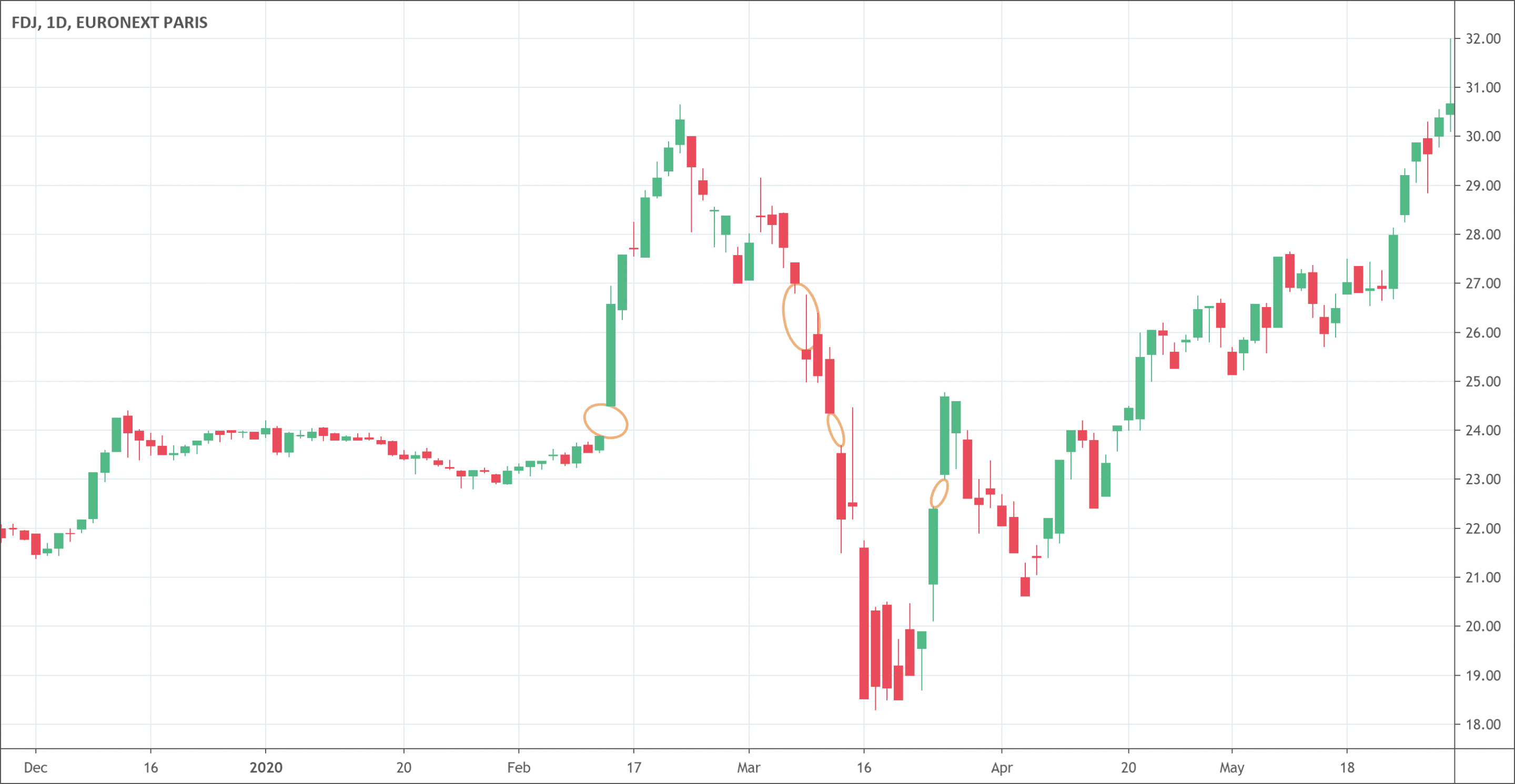
- A gap appears on the technical analysis chart when there is a unfilled area.
- It shows there was no trading activity in that area.
- It happens when price closes at a level and open at a different level (higher or lower).
- There are different types of gaps: breakaway gap, common gap, exhaustion gap and continuation gap.
What is a gap?
A gap is an unfulfilled area on the technical analysis chart that shows there was no trading activity in that area. Zero tradings within a particular price range occur between the closing point of one day’s market and the opening of the next day’s. Gaps is a common term used in technical analysis further divided into two, gap up and gap down. When the low price after the closing of the market is higher than the high price of the last day, it forms an up gap. On the other hand, if the high price after the closing of the market is lower than the low price of the last day, it forms a down gap. Traders generally consider an up gap as bullish and a down gap as bearish.
A pertinent question arises here that why do the market gaps occur in the first place? The answer is quite a simple one. It is in fact a matter of common sense. Financial market gaps arise whenever the market presents something unexpected because of an event or a related event occurring somewhere in the world. For example, after a win in the election by an unexpected party affects the market as it happened recently when European recovery was badly affected by the possibility of an anti-austerity party coming into power in Italy.
Market gaps may also occur as a result of significant selling pressure. The selling pressure causes stock prices to go lower on the opening from the closing of the previous day. It indicates the control of sellers. An imbalance in the supply and demand also causes market gaps.
What does the market gap tell traders?
The market gap tells traders about the price movement. It tells traders about something important happening to the fundamentals or the psychology of the traders. These gaps are in the limelight since the inception of the technical analysis. They are extremely helpful in financial trading because they make the market’s picture very clear.
Types of market gap patterns
There are four most common and widely used types of market gap patterns.
- The breakaway gaps that occur at the end of a price pattern indicating a break-up or break down. The breakaway gaps are very popular for indicating a change in direction or a new trend.
- The common gap is the gaps that represent the trader’s preferred trading area of the price gap. It tells traders a precise area of the price gap where traders can apply their gap trading strategy.
- The exhaustion gap is a kind of final leg of a price pattern indicating the final attempt of the market to touch new highs or lows of the prices. The exhaustion gaps are the fundamental patterns to predict the reversal of bearish patterns or the reversal of bullish patterns.
- The continuation gap occurs right in the middle of the financial asset’s price pattern. This is a unique gap that indicates the psychology of a group of traders, buyers or sellers, who believe that the stock is heading in a particular direction. The continuation gap is perfect for traders who need full confirmation first to enter a trade.
How to devise a prudent gap trading strategy?
As we have already discussed that the market gaps have always been a part of technical analysis and trading since the inception. Different traders devise different gap trading strategies to take full advantage of the market gaps. For example, most traders tend to buy whenever fundamental or technical factors favor a gap such as a positive earnings report will favor a gap up the next day. Traders may also base their gap trading strategy on hopes or predictions about a good fill of the gap or a continuation of a trend. The following are some other popular market gap trading strategies.
- Sell short and place a stop-loss a few points higher than the upper rim of the gap when you observe a breakaway gap. It is also prudent to go long and place stop-loss a few points below the lower rim of the gap. However, it is also a key to watch for volume. High volume is a must for successful trading of a breakaway gap.
- Traders tend to cover shorts immediately, by placing the stop-loss above the high, upon observation of an exhaustion gap. Being watchful of the volume is crucial here as well because the low volume is necessary while trading an exhaustion gap.
- Going short and place a stop loss a few points above the upper rim of the gap upon observation of a continuation trend.
However, for successful market gap trading, it is important to correctly identify the gap that you are going to trade. The gaps are also affected by the trading policies of retail and institutional investors. Retail investors are the most common players in this regard because of their irrational exuberance. Therefore, it is important to wait for the break of the prices before taking a trading position.
Conclusion
The market gaps are very popular for being extremely helpful in technical analysis. They portray a very vivid and clear picture of the financial markets. A market gap represents a blank area on the chart indicating zero trading activity in that particular area. It is crucial, however, to identify the gaps correctly because the market gap can be a genuine one or it may be a phony one. A genuine market gap occurs after the market skips a price level. A phony gap occurs when asset trades in another market while the market trader is analyzing has closed. There are multiple trading strategies that traders can employ according to their overall trading strategy. However, successful gap trading depends on the correct classification of the market gap.
 Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
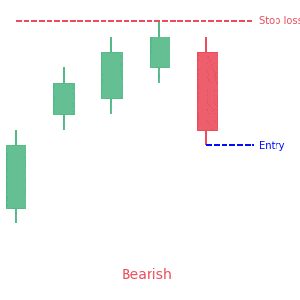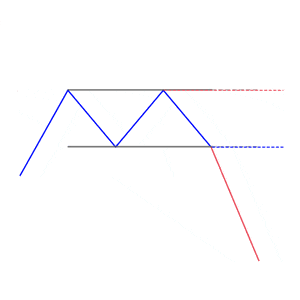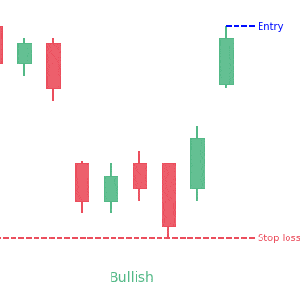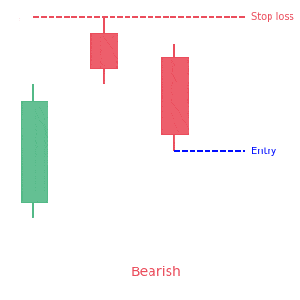 We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!
We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!