Stop-loss calculation is absolutely imperative for the long-term success of a trader. Probably, traders shouldn’t even think about trading without it. In fact, if you are serious about your trading endeavor and want to achieve success, forget about entering even a single trade without proper stop-loss calculation.
Given the importance of stop-loss orders, we decided to help you in this aspect of trading as well. Today’s guide on stop-loss calculation is going to explain the best practices to calculate your stop-loss. Let’s dive deep and find out what lies ahead of us.
Stop-loss – what is it?
A stop-loss order is a type of order that automatically closes an open trade when the price reaches a predetermined level. Traders specify that when the price of a financial instrument goes above or below a certain price level, their position should be closed to prevent too many losses. Thus, stop-losses empower traders to exit losing positions before incurring too many losses.
So, stop-losses are orders that enable traders to keep their positions open without risking too much capital. We can say that they help traders in risk management. For example, you decide to go long on the stock of a company XYZ. Now suppose that $45 per share is the current price of XYZ’s stock. So, where will you put stop-loss to prevent risking too much? Let’s say that you want to exit your position if the price goes below $40. Therefore, you can put a stop-loss at $39.99.
Why are stop-losses important?
As you know, stop-losses help in risk management. They are very important risk management tools that automatically close a losing trade. Thus, it helps you prevent incurring too much loss. In short, if you are venturing into a volatile market, stop-losses help you prevent large and uncontrollable losses. Contrarily, if you don’t use this tool, you may end up losing a significant portion of your account in case of a large position getting uncontrollable.
That said, always using stop-loss is a prerequisite to success in trading. As you know, proper risk management is even more important than getting profits. Only stop-losses can help you stay in the game for the long term and protect your capital.
Additionally, stop-losses also help in other risk management techniques. For example, they help in deciding position size, how much to risk on a single trade, how much to risk for a potential single dollar profit, and much more. Simply put, stop-loss should be a key part of your overall trading strategies.
Stop-loss calculation
After learning about the importance of stop-losses, it’s time to learn how to calculate your stop-loss. There are two best practices for stop-loss calculation.
- Cents or pips at risk
- Account dollars at risk
Although there are two techniques for stop-loss calculation, the account dollars at risk strategy is more useful. It provides more vital information as it helps you to determine how much of your money you risk on a single trade.
Furthermore, if we go into further detail, there are numerous theories about stop-loss calculation and placement. For example, you may find some theories emphasizing a fixed percentage such as 6% on all financial instruments. Let’s suppose that you have shares of a company currently priced at $30 per share. Now, $28.20 ($30 – 6% of $30) will be your stop-loss when using a strategy with a 6% rule. However, there are other strategies also that focus on security-specific or pattern-specific techniques. But the fact is, it all depends on how much money you want to risk for a single trade. For example, if you are comfortable with putting 20% of your account at risk, you may go ahead. However, it is important never to risk too much as staying longer in the game requires you to preserve your capital.
Stop-loss calculation – other strategies
There are other strategies as well that don’t require stop-loss calculation. These strategies only require you to place stop-loss at key price levels. These strategies are;
Support and resistance levels
Key support and resistance areas on your chart are the most effective points for stop-loss placement. Firstly, you need to learn how to correctly identify these key areas on your chart. Support is the area that stops prices from falling further and supports them. Whereas, resistance is the level that stops prices from rising above it.
Secondly, you can place stop-losses above or below key resistance or support levels respectively. For example, if you are going short, you can place stop-loss a few points above the key resistance area. Conversely, you can put stop-loss below a key support area when going long. However, it is important to wait for confirmation as big market players may hunt your stop-losses and cause significant losses.
Furthermore, key areas on your charts aren’t only support and resistance areas. There are several other areas such as channels, trendlines, pivots, and so on.
Trend following
Trend followers use trailing stop-losses. A trailing stop-loss is the one that automatically trails each tick of price that moves in a trader’s favor. For stop-loss calculation when using trend following strategies, you need to measure two distances. Firstly, you need to measure the distance between the higher high and higher low. Secondly, measure the distance between lower highs and lower lows. Thus, it allows you to set your stop-loss with an average distance of the correction move of a trend. This strategy is quite useful as you stay within the trend and a trailing stop automatically locks profits in during the trend.
Locking in profits
In stop-loss calculation using this technique, you need to move your stop-loss after some basic calculations. For example, you may calculate your break even point to place a stop-loss. Then calculate 33% of the total price if the price goes further above. Then calculate 66% and so on.
This strategy involves moving your stop-loss to lock in profit when enjoying a profitable trade. However, this strategy involves moving your stop-loss manually.
Stop-loss calculation – an important point
Surely, you would love to make a larger profit than your potential loss. Isn’t it? Great! That’s what you must expect just like experienced traders. Experienced traders always set profit targets wider than their stop-losses. Therefore, you should keep this in mind during the stop-loss calculation process.
The risk and reward ratio is the key here. For example, if you risk $1 to make a $1 profit, then you are making a huge mistake. This strategy will cause huge losses in the future. Conversely, if you are going with a strategy that involves risking $1 to make a profit of $3, it means the risk/reward ratio is 1:3. Although this ratio offers a success rate below 50%, it earns you hefty profits. That said, it is important to choose a risk/reward ratio that suits you. Afterward, use this ratio for stop-loss calculation. And you also need to keep in mind that your profit target must be wider than your potential loss.
The wrap-up
Stop-loss calculation is a prerequisite to the long-term success of a trader. Trading without stop losses means risking your entire capital. Therefore, it is important to learn about stop-loss calculation. There are several strategies to calculate stop-losses. Additionally, there are also techniques to choose stop-losses without stop-loss calculation. For example, you can use key price levels such as support and resistance levels on your charts to place stop-losses.
Furthermore, how you calculate stop loss also depends on your risk appetite and risk management strategy. However, you need to give it proper consideration if you want to stay in the game for longer.
 Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
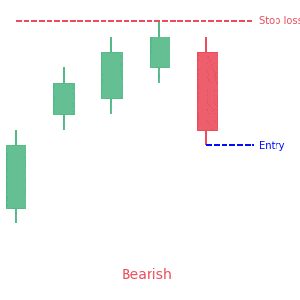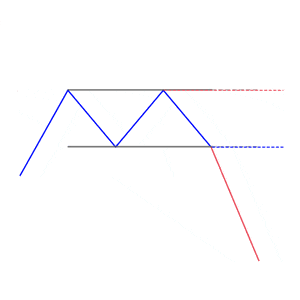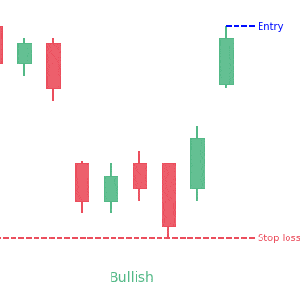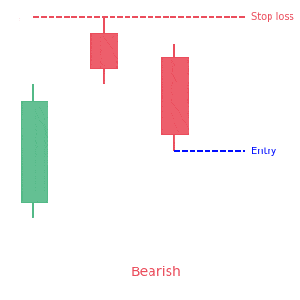 We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!
We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!