Regardless of whether you are not a stock merchant, you presumably realize that the financial exchange doesn’t open all week long, which can restrict the amount of days one can exchange during a year.
Considering that, you might think about the quantity of exchanging days there are in a year. Anyway, what number of exchange days are there each year?
As indicated by the U.S. securities exchange, the normal number of exchanging days is around 252; in any case, this number might fluctuate from one year to another since few out of every odd year has 252 exchanging days. In 2020, there are 253 exchanging days, while in 2021; there are going to be 252 exchanging days.
Many elements can influence how frequently you exchange, which is the reason, in this post, we will talk about why exchanging days change, who sets the exchanging plan, and different elements. We should start by characterizing an exchanging day.
How does a Trading Day Work?
Trading days are any days on which the property exchange is permitted for trading. Usually, the exchange is permitted on Monday to Friday, except for major holidays or events that prevent the exchange from being open.
The market is open during normal trading times rather than electronic or elongated trading times.
From 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. Eastern Time, the NYSE and Nasdaq Exchange hold regular trading hours.
Opening bells ring at the start of each trading day, and closing bells ring at the end. As soon as the bell for closing sounds, all share dealing ceases and the next dealing day starts.
It’s not uncommon for stock markets to be closed on weekdays even though they’re usually open Monday through Friday. The market is closed on public holidays and days programmed for state functions, such as state funerals for heads of state.
Other unique events could cause the market to close at 1:00 PM rather than 4:00 p.m, resulting in a shorter trading day.
Number of Trading Days per Year
During normal trading hours, the Nasdaq and New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) operate from 9:30 a.m. through 4:00 p.m. Eastern Standard Time.
Stocks can also be traded in the pre-market and after-hours markets, although the majority of shares are traded during normal hours.
Trading takes place in the pre-market from 8:00 a.m. until 9:30 a.m. Eastern Time. It is possible to trade stocks after-hours from 4:00 to 6:30 p.m. Eastern Time.
These extended trading hours give some investors an edge over the competition because they allow them to react more quickly to news releases outside the regular trading hours.
What is the amount of trading days yearly? In any given year, there are 252 trading days on the U.S. stock market out of 365, which breaks down to 4.85 trading days a week.
Market Holidays
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or Nasdaq Stock Market (Nasdaq) closes on a nonweekend day.
This holiday usually falls between New Year’s and Christmas. On Saturdays and Sundays, public holidays entail two rules that govern market closures:
- Markets will close on the preceding Friday if the holiday falls on a Saturday.
- The markets will close on the Monday following a holiday that falls on a Sunday.
- The stock market remains open during some holidays and days near them.
Historically, the markets have closed all or part of their session for a funeral of an American president, including in 1994 when they closed for a full day following Richard Nixon’s funeral and in 2004 following Ronald Reagan’s death.
Stock markets can also be closed for reasons other than holidays, such as serious technical difficulties with a stock exchange’s trading platform, terrorist attacks, or extreme weather events.
What will the Number of Stock Trading Days be in 2021?
In 2021, there will be 252 trading days (forex and stock trading days) out of 365 possible days; 104 will be weekends (Saturday and Sunday) when the stock exchanges are closed.
On Friday, July 3, Independence Day, one of nine holidays that end the exchanges, falls on a weekday. In November 2021, there will be one shortened trading session.
Calculating Number of Trading Days from Historical Data
By using daily historical data of some security or index which you are sure to have traded every day in the period you want to refer to, you can easily determine the number of exchanging days per year for your market.
The best candidate would be a local broad-market stock index since that would be calculated every day the exchange is open. The S&P500 or DJIA indexes in the US are a good starting point for the VIX for those interested in options.
The daily historical data for these indices is also widely accessible (from the exchange or index provider directly or, for example, from Yahoo Finance).
After you collect the data, all you need to do is count the days for each period (number of rows with daily data) and divide the total by the number of years.
Avoid These Common Mistakes
1. Don’t leave any gaps in your data.
2. Make sure there are no duplicate entries. The data provider may have made a technical error (writing the same day’s data twice), or notes might be inserted into some rows. Clean the data before using it.
3. For the first and last year you include in your calculation, make sure the data is from the very beginning (normally the first trading day of the year is on 2 or 3 or 4 of January) to the very end (end of December). Please do not use the last year you have, which is likely incomplete and will distort the results downward.
4. Use Excel’s COUNT function to count the days. Subtracting the first date from the last date defeats the purpose of the calculation – your number will include all calendar days, not just trading days.
5. Don’t just subtract the last year from the first year when counting the number of years (so that you can divide the days by it).
Who is Responsible for Setting the Trading Schedule?
The main stock exchange in each country sets the trading program for its stock market. For both days and hours traded, the NYSE sets the trading calendar in the United States, while most other markets follow it.
The NYSE used to hold a 2-hour trading session on Saturdays together with the regular trading schedule Monday through Friday, but from 1952, U.S. exchanges such as the NYSE have sustained a 9:30 AM. until 4 PM ET trading schedule Monday through Friday.
People from other time who desire to exchange on the NYSE must do so during the NYSE’s trading day calendar, which is based on New York time zones.
The trading can be done remotely through electronic trading platforms, but it must be done during the programmed trading hours. If you are not in the ET Zone, you will need to enter the market between 9:30 AM and 4:00 PM ET.
Why do Trading Days Vary from Year to Year?
The number of days for trading varies a little yearly, as we stated earlier. According to several years, it will be 252 days, though it can also be 253 days or 251 days; it depends on various factors. The number of dealing times in a year can be affected by many factors, such as:
- During the holidays
- Over the weekend
- Events of importance
- Leap year
 Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
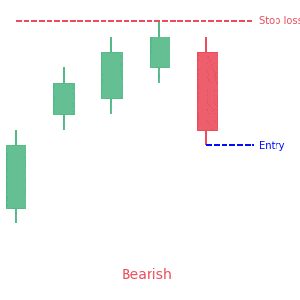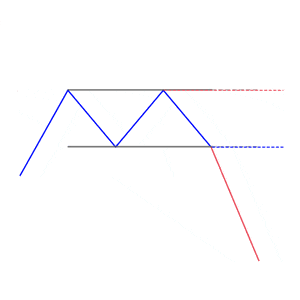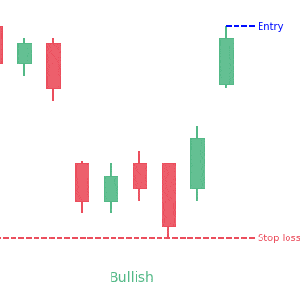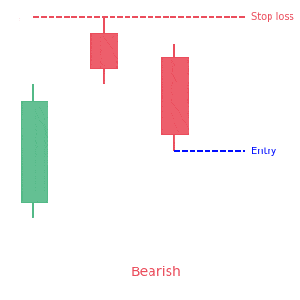 We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!
We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!