- The stochastic oscillator is a popular momentum technical indicator.
- It gives traders overbought and oversold signals.
What is the Stochastic indicator?
The Stochastic Oscillator is a momentum indicator
A stochastic oscillator is a momentum indicator that compares a specific closing price of a security or trade to a range of its prices over a certain period. Traders can reduce the sensitivity of the oscillator to market movements by adjusting that time or by taking a moving average of the result. It creates overbought and oversold trading indicators, using a 0-100 bounded range of values.
George C. Lane developed the stochastic indicator in the 1950s, and it shows the position of the most recent closing price relative to the previous high-low range. It measures momentum by comparing the closing price with the previous trading range over a specific period.
The Stochastic Indicator follows the momentum of the price
The indicator doesn’t follow the price or volume of the underlying currency pair, but the momentum of the price. This entails that the stochastic indicator switches direction before the price itself and can be considered an important indicator.
The most vital signals that it identifies are the bearish and bullish divergences that appear on the stochastic indicator. This can anticipate a price reversal. Also, as the stochastic indicator oscillates within a range, traders can use it to detect overbought and oversold price levels.
Even though the stochastic indicator can be used in all financial markets, it is particularly famous among forex traders. The stochastic oscillator makes use of a scale to measure the amount of change between prices from one closing period to predict the continuation of the current direction trend. The two lines are similar to the MACD lines because one line is faster than the other.
The oscillator works on this theory:
- When there’s an uptrend, prices will remain equal to or above the previous closing price
- When it’s a downtrend, prices will probably remain equal to or below the previous closing price
Before getting into using the stochastic, it is important that we are clear about what momentum actually is. So, what is momentum? According to Investopedia, it is the rate of acceleration of the price of a security.
What does the Stochastic Oscillator tell traders?
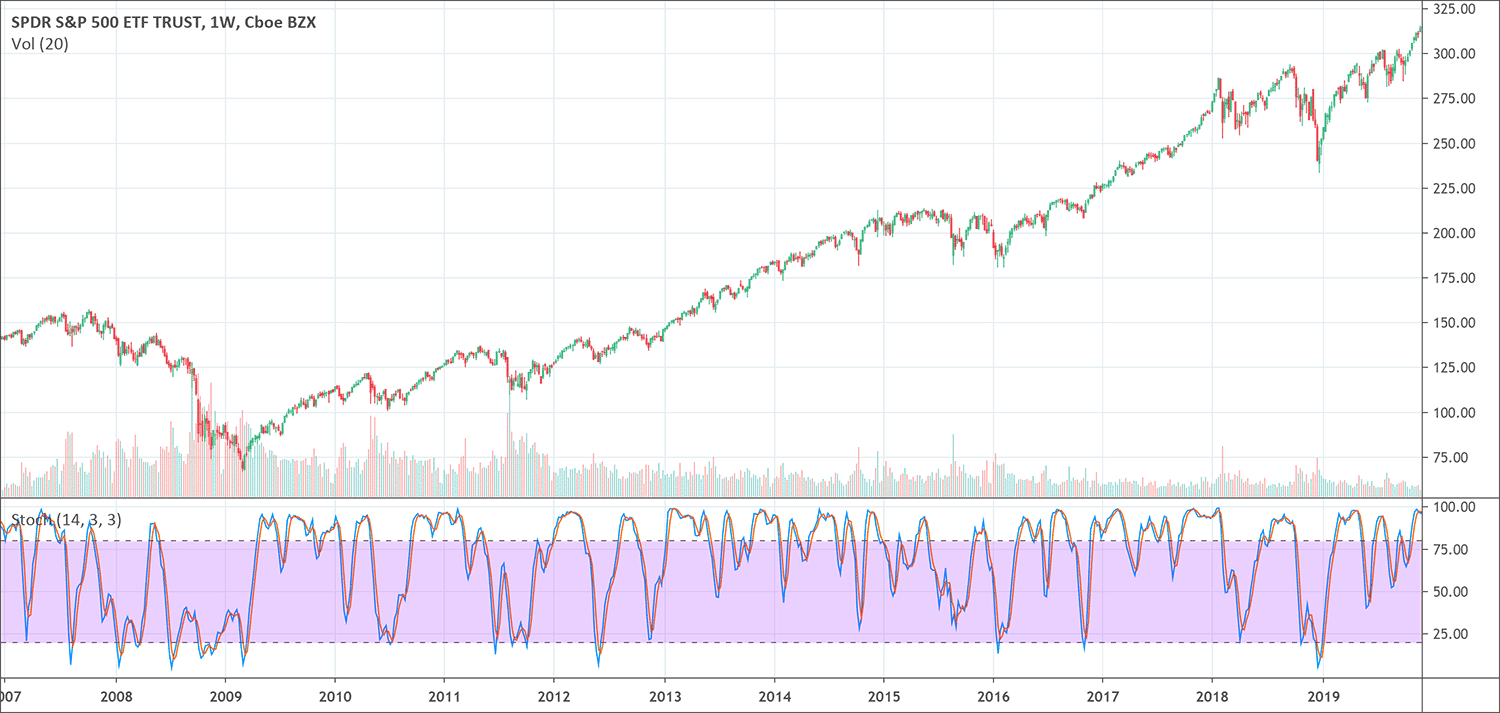
The stochastic oscillator is range-bound; this means that it is always between 0 and 100, making it an important indicator of overbought and oversold situations. Traditionally, readings beyond 80 are seen in the overbought range, and readings below 20 are seen as oversold. But these are not always indicative of an impending reversal; very strong trends can sustain overbought or oversold conditions for a long time. Rather, traders should look to changes in the stochastic oscillator for ideas about future trend movements.
Two lines usually make up this charting:
- one showing the real value of the oscillator for every session,
- and the other reflecting its three-day simple moving average.
Since price is thought to follow momentum, intersection of these two lines is an indication that a reversal is likely on its way. It shows a huge shift in momentum from day to day.
Traders consider the divergence between the stochastic oscillator and trending price action is also a vital reversal signal. For instance, when a bearish trend gets to a new lower low, but the oscillator prints a higher low, it may be an indicator that bears are exhausting their strength and a bullish reversal is on the way.
How to use the Stochastic indicator?
When using the stochastic oscillator to identify overbought and oversold market conditions, a reading above 80 means overbought market conditions and a reading lower than 20 shows an oversold market condition. The stochastic indicator itself can range only from 0 to 100, no matter how fast the price of the underlying currency pair changes. In a standard setting, a reading above 80 signifies that the pair has been trading close to the top of its trading range while a reading below 20 means that the pair has been trading near the low of its trading range.
Keep in mind, oversold readings are not necessarily bullish, just like overbought readings are not necessarily bearish. When there’s a sustained period of uptrend or downtrend, the stochastic indicator can stay in the oversold or overbought area for a long period.
It is, therefore, advised to trade in the direction of the trend and wait for occasional oversold readings during uptrends and overbought readings during downtrends.
Bullish and bearish divergences
Divergences appear when a new high or low is not confirmed by the stochastic oscillator. When price records a lower low, but the stochastic oscillator makes a higher low it prints a bullish divergence. This indicates less downside momentum that could foreshadow a bullish reversal.
When price sees a higher high, but the stochastic oscillator makes a lower high it creates a bearish divergence. This indicates less upside momentum that could foreshadow a bearish reversal. Once a divergence happens, chartists should look for a confirmation to indicate an actual reversal.
A bearish divergence can be confirmed with a support break on the price chart or a stochastic oscillator break lower than 50, which is the midpoint. A resistance break on the price chart or a stochastic oscillator break over 50 can confirm a bullish divergence.
Biggest mistakes to avoid for traders with the Stochastic Oscillator
The stochastic technical indicator tells traders when the market is overbought or oversold. Lines are above 80 means the market is overbought and lines below 20 mean that the market is possibly oversold. Generally, it is best to buy when the market is oversold, and sell when the market is possibly overbought.
Pros & Cons
Traders need to understand where the stochastic oscillator acts best and where its short-comings are, to get the most out of the indicator.
Pros
- It has clear entry and exit signals
- Its signals come up frequently, depending on your selected time setting
- This indicator is available on most charting packages
- It is conceptually simple to understand
Cons
- It can generate false signals when incorrectly used. This is when it generates a trading signal, yet the price does not follow through, which can end up as a losing trade. This can happen regularly during a volatile market condition. One way of handling this is to take the price trend as a filter, where indicators are only used if they are in the same direction as the trend.
- If a trader trades against a trend, the prices may remain overbought or oversold for a long time
Conclusion
Even though momentum oscillators are best for trading ranges, traders can use them with securities that trend, given that the trend takes on a zigzag appearance. Pullbacks are part of uptrends that zigzag higher. Bounces are part of downtrends that zigzag lower. Because of this, traders use the stochastic oscillator to detect opportunities in harmony with the bigger trend.
The indicator helps to see turns close to support or resistance. If you have a security trade close to support with an oversold stochastic oscillator, look for a break above 20 to indicate an upturn and successful support test. Conversely, if a security trades close to resistance with an overbought stochastic oscillator, notice for a break below 80 to indicate a downturn and resistance failure.
The settings on the stochastic depend on personal preferences, timeframe and trading style. A shorter look-back period will make a choppy oscillator with a lot of overbought and oversold readings. A longer look-back time will give a smoother oscillator with few overbought and oversold readings.
Like most technical indicators, it is necessary to use the stochastic oscillator together with other tools for technical analysis. Breakouts, volume, and support/resistance levels (and other signals) confirm or refute signals made by the stochastic oscillator.
 Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
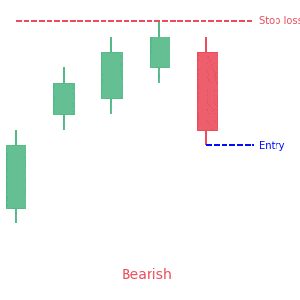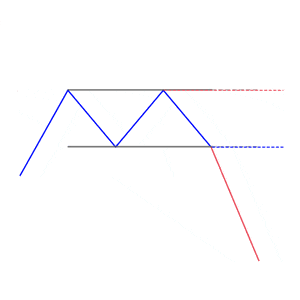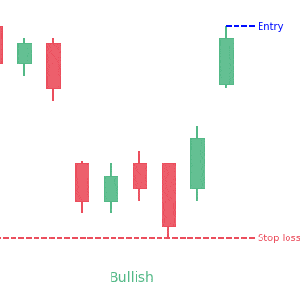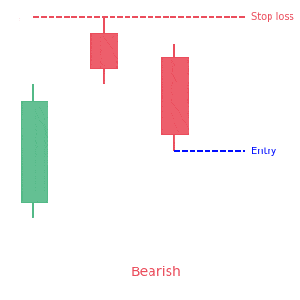 We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!
We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!