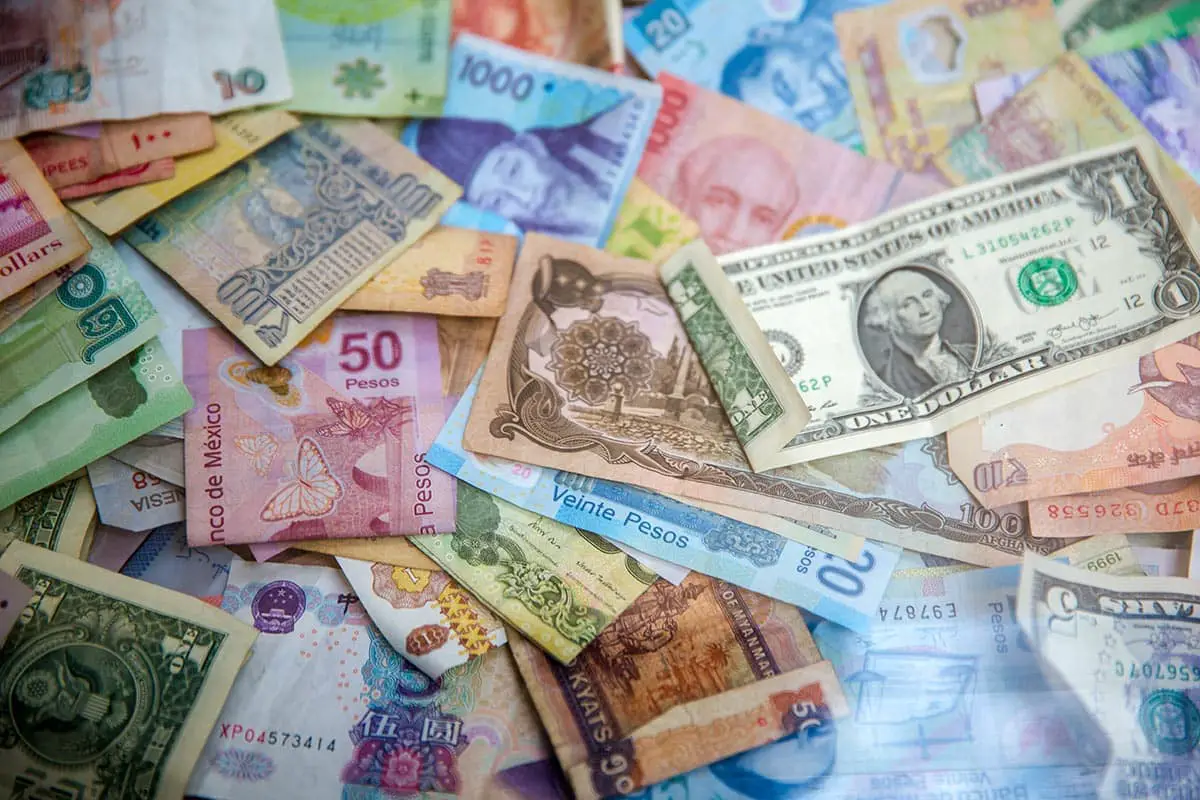
- Forex markets let traders exchange currencies
- It can take various forms from real currencies to derivates
- These markets are often very liquid and are traded 24h-5days a week
The foreign exchange market or forex (FX) is a decentralized marketplace to buy or sell different currencies. It is a decentralized market because trading here takes place over the counter through the interbank market. Hence, there is no use of a centralized exchange here.
Forex trading over Forex markets has become very popular. In fact, it has become a phenomenon of this century. Forex markets attract traders from all across the globe because of:
- FX market’s size
- Almost all major fiat currencies are available for trade
- The most liquid market in the world
- Easy to find buyers and sellers for foreign exchange
- Volatility levels differ
- Minimum transaction costs
- 24/5 trading
Types of forex markets
There are three major types of forex markets.
Spot forex markets
Spot forex markets offer a physical exchange of currencies on the spot and instantly settle the trade.
Forward forex markets
It works on the basis of a contract to buy or sell currency at a specific price at a specified date in the future.
Futures forex markets
Futures forex markets offers exchange-traded contracts to sell or buy a specific currency amount at a specified price and date in the future.
How do the forex markets work?
Foreign exchange markets work on the same mechanism as the markets do. That means forex markets are also subject to supply and demand. For example, whenever there is a strong demand for USDs from British citizens having Pounds, they will get USD in exchange for Pounds. As a direct result of this exchange, the value of USD will rise while the value of GBP will fall. Here, it is important to note one thing. This transaction will only affect the GBP/USD currency pair. It will not cause any other currency to fall or rise against GBP/USD.
Factors affecting the forex market
There are various factors that affect and move the FX markets. The first one is an exchange of currency pairs where one rises at the expense of the other’s fall. Successful traders always make the most of the economic calendar and other such factors that affect the FX market.
- Other factors might include:
- Broad macroeconomic factors like big news or events such as success in the election of a new political party
- Country specific factors like inflation, GDP, interest rate, etc.
Forex trading and how does it function?
After a brief introduction to foreign exchange markets, let us proceed to forex trading and how does it work. All and sundry often wonder how to make money through currency trading and forex trading. Fortunately, forex trading isn’t rocket science as most people think. It is quite easy and straightforward. Forex trading works on a very simple mechanism, going long and short. You buy the currency when you think this currency will go up. It is known as going long. You sell the currency when you think this currency will fall. This is known as going short.
Types of forex traders in forex markets
There are two basics types of forex traders in foreign exchange markets, hedgers and speculators. Hedgers are the safe players of currency trading who always look to avoid extreme exchange rate movements. They reduce their exposure to foreign currency movements. For example, you can study big conglomerates like Exxon.
On the other hand, speculators are risk seekers and always look to capitalize on volatility in exchange rates. These players are always on the move to take full advantage of exchange rate movements. Retail traders and big trading desks at big banks are prime examples of speculators.
Types of forex currency pairs
There are four major types of forex pairs for currency trading.
- Seven currencies that make 80% of forex trading all over the world are major currency pairs. EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and USD/CHF are among the major pairs.
- Minor pairs include pairs featuring other major currencies against each other excluding the USD. These are infrequently traded pairs and include EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY, and EUR/CHF.
- Exotic pairs include currency pairs from major currencies against currencies from emerging economies. They include EUR/CZK, GBP/MXN, USD/PLN, etc.
- Regional pairs include currency pairs bounded by regions and include AUD/SGD, EUR/NOK, AUD/NZD, etc.
How to read a forex quote?
It is crucial for all FX market traders to understand how to read a forex quote. Forex quote determines the price at which you enter or exit the trade. For example, in a EUR/USD currency pair, the first currency is the base currency which is Euro. The second currency is known as variable or quote currency which is USD.
Almost all foreign exchange markets offer currency prices up to five decimals. However, the first four decimals are the most important. Let us suppose that USD has a 1.13528 selling price in this EUR/USD pair. Here, 1 (the number on the left side) is one unit of quote currency. The first two decimal digits are cents which are 13 US cents in this case. The following digits are fractions of a cent known as pips. If the EUR falls against the USD by 200 pips, the new sell price reflects the lower price of 1.11528. Hence, the cost to buy EUR will be less in USD.
Why you should try forex trading?
Forex trading offers more opportunities to gain as it allows forex traders to take different speculative positions. It also offers several currency trading pairs to traders to spot profitable trades. Forex trading also has several advantages over the trading in other markets such as:
- Low transaction costs: That means forex trading is less expensive. It offers low transaction costs as compared to other markets with high commission costs.
- Leverage trading: Forex trading is leverage trading as it doesn’t demand from traders to pay the full cost of a trade. Traders only need to pay a fraction of the cost.
- Low spreads: Spreads are very low for all major currency pairs because of liquidity. Spread becomes the first and foremost hurdle that demands to be overcome during successful trading. When the spread is low, you have all the additional pips as profit.
Key forex trading terms explained
Bid price
The bid price is the highest price of a currency that a buyer willingly pays. A seller sees the bid price generally to the left of the quote and is usually in red.
Ask price
The ask price is the inverse of the bid price. Hence, it is the lowest price a seller willingly accepts. A buyer sees the ask price generally to the right and is usually in blue.
Spread
Spread means the difference between the bid price and the ask price. The spread of a forex market represents the actual spread of a forex market plus the additional spread that a broker adds.
Leverage
Leverage in a forex market represents a fraction of the total value of a trade that a trader puts up. It makes forex trading easy by allowing traders to trade bigger positions with low capital. Leverages can maximize profits as well as losses.
Margin
Margin means the minimum capital that traders require to initiate a leverage position. It is a difference between a trader’s full value and the funds provided to that trader by a broker.
Margin call
Margin call means the dipping below margin requirements of your capital plus or minus profit or loss. The margin requirement is a predetermined specified level.
Liquidity
Liquidity in forex trading means how easy you get a buyer or seller in the market for your currency pair. It is because of thousands of active participants in the foreign exchange markets trading that currency pair.

 Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
Good Trading requires the Best Charting Tool!
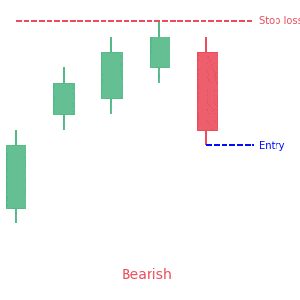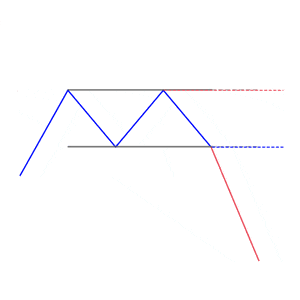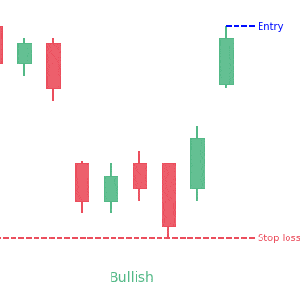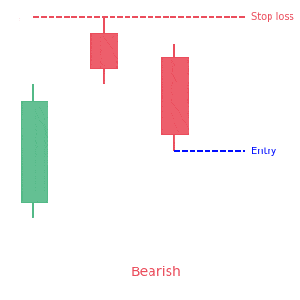 We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!
We loved Marwood Research’s course “Candlestick Analysis For Professional Traders“. Do you want to follow a great video course and deep dive into 26 candlestick patterns (and compare their success rates)? Then make sure to check this course!